Horizontal Scaling Deployment Strategies
Weaviate offers two complementary superpowers for scaling your deployment: sharding and replication. Sharding divides your data so it can be spread out across multiple nodes, allowing you to handle datasets far larger than a single machine could process. Meanwhile, replication creates redundant copies of your data, ensuring high availability even when individual nodes fail or need maintenance. While each scaling method shines on its own, the true magic happens when they join forces.
Let's explore how you can harness these capabilities to build a deployment that's both massive in scale and rock-solid in reliability!
Scaling Methods
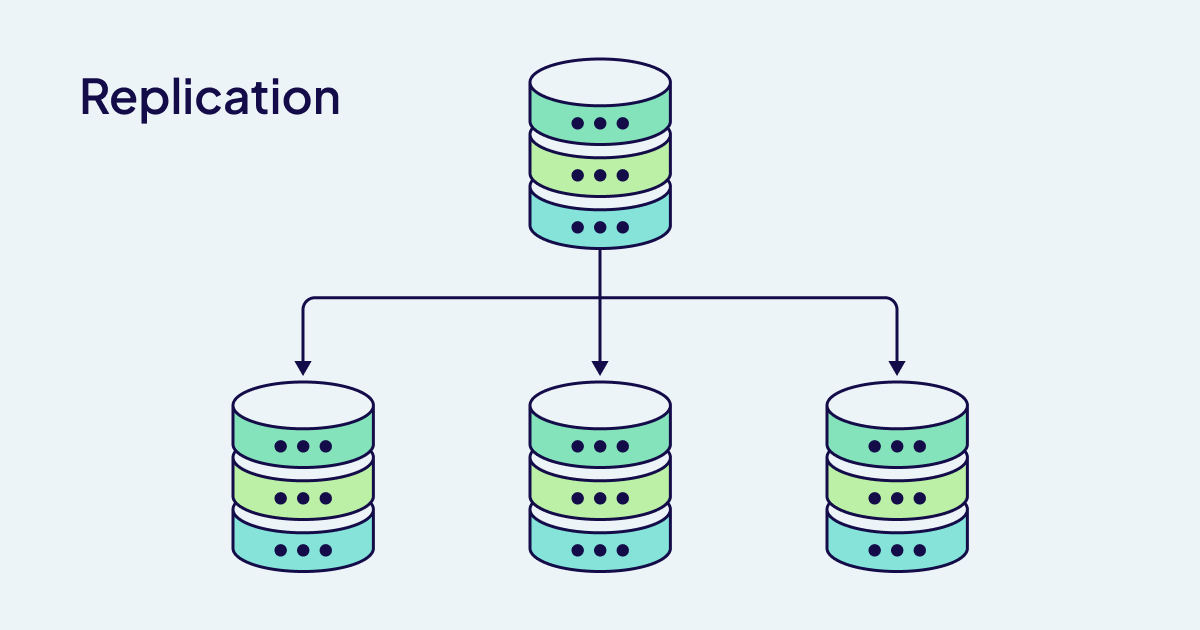
Replication
Replication creates redundant copies of your data, it is useful when your data needs to be highly available.
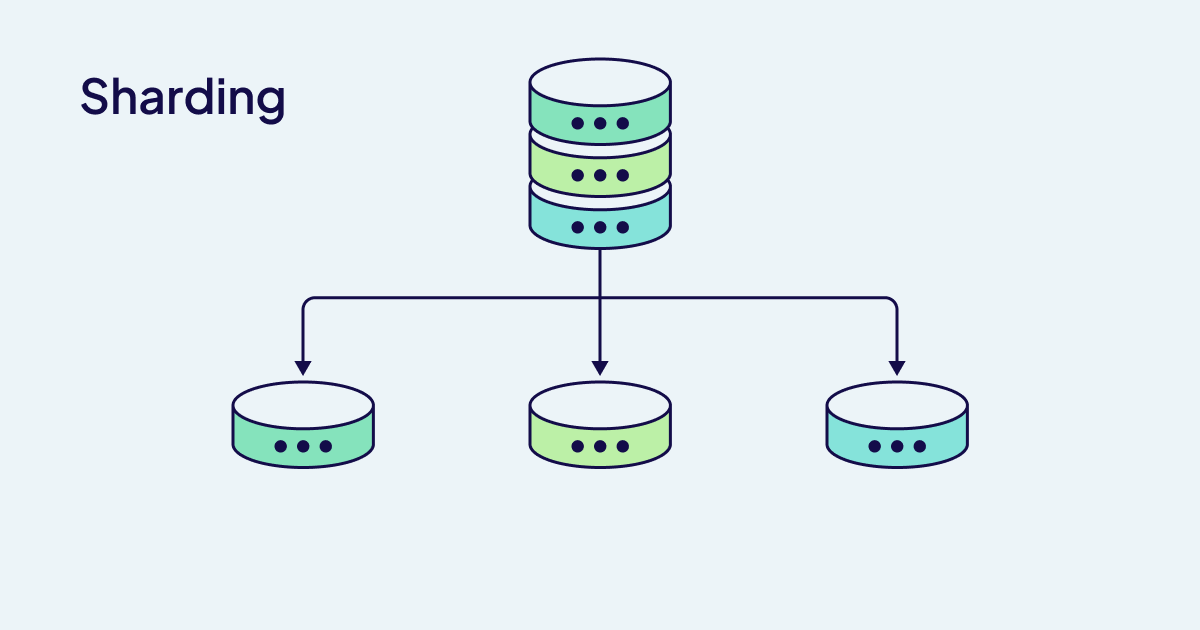
Sharding
Sharding divides data across nodes, it is useful when your dataset is too large for just a single node.
Choosing your strategy
| Requirement/Goal | Sharding | Replication | Both Combined | Primary Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handle dataset too large for single node | Yes | No | Yes | How much data are you storing?
|
| Improve query throughput | Maybe* | Yes | Yes | Is your workload read-heavy?
|
| Accelerate data imports | Yes | No | Yes | Is import speed a priority?
|
| Ensure high availability | No | Yes | Yes | Can you tolerate downtime?
|
| Enable zero-downtime upgrades | No | Yes | Yes | How critical is continuous operation?
|
| Optimize resource utilization | Yes | Maybe* | Maybe* | Are you resource-constrained?
|
| Geographic distribution | No | Yes | Yes | Do you need multi-region support?
|
*This may serve as a partial solution and will depend on your configuration.
Sharding: Divide and Conquer
You've made the decision to shard your data, now let's get it configured:

If a snippet doesn't work or you have feedback, please open a GitHub issue.
from weaviate.classes.config import Configure
client.collections.create(
"Article",
sharding_config=Configure.sharding(
virtual_per_physical=128,
desired_count=1,
desired_virtual_count=128,
),
)
Parameters
These parameters are used to configure your collection shards:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
desiredCount | integer | Immutable, Optional. Controls the target number of physical shards for the collection index. Defaults to the number of nodes in the cluster, but can be explicitly set lower. If set higher than the node count, some nodes will host multiple shards. |
virtualPerPhysical | integer | Immutable, Optional. Defines how many virtual shards correspond to one physical shard, defaulting to 128. |
desiredVirtualCount | integer | Read-only. Shows the target total number of virtual shards, calculated as desiredCount * virtualPerPhysical. |
Replication: An army of clones
Configure your data's replication to ensure it's always available:
The replication factor of a collection cannot be updated by updating the collection's definition.
From v1.32 by using replica movement, the replication factor of a shard can be changed.
Configure replication settings, such as async replication and deletion resolution strategy.

If a snippet doesn't work or you have feedback, please open a GitHub issue.
from weaviate.classes.config import Configure, ReplicationDeletionStrategy
client.collections.create(
"Article",
replication_config=Configure.replication(
factor=3,
async_enabled=True, # Enable asynchronous repair
deletion_strategy=ReplicationDeletionStrategy.TIME_BASED_RESOLUTION, # Added in v1.28; Set the deletion conflict resolution strategy
),
)
In a highly available environment, combining sharding and replication leverages the power and
capabilities of both methods to be a dynamic duo that keeps your deployment highly available.
If given the opportunity, those two techniques will be your deployment's dynamic duo.
Specifically using the ASYNC_REPLICATION environment variables introduced in the 1.29 release
will allow you to unleash the full power of horizontal scaling!
Questions and feedback
If you have any questions or feedback, let us know in the user forum.
