Manage collections
Use the following guides for detailed instructions and concepts related to specific Weaviate features. Learn how to perform basic collection operations, configure vectorizers, integrate models, implement multi-tenancy or multi-node setups, migrate data, and manage cross-references.
Learn how to create, read, update, and delete collections.
Configure a vectorizer (embedding model), vector indexing parameters, and related settings.
Configure the inverted index for efficient keyword searches and filtering.
Integrate Weaviate with various model providers like OpenAI, Hugging Face, Cohere, etc.
Isolate data for different tenants within a single Weaviate instance.
Set up and configure Weaviate for high availability and scalability across multiple nodes.
Use aliases to switch between collections without changing your application code.
Set a time-to-live (TTL) for objects to automatically expire and be deleted.
Learn strategies and steps for migrating your data schemas and objects.
Define, manage, and query relationships between objects.
How collections work
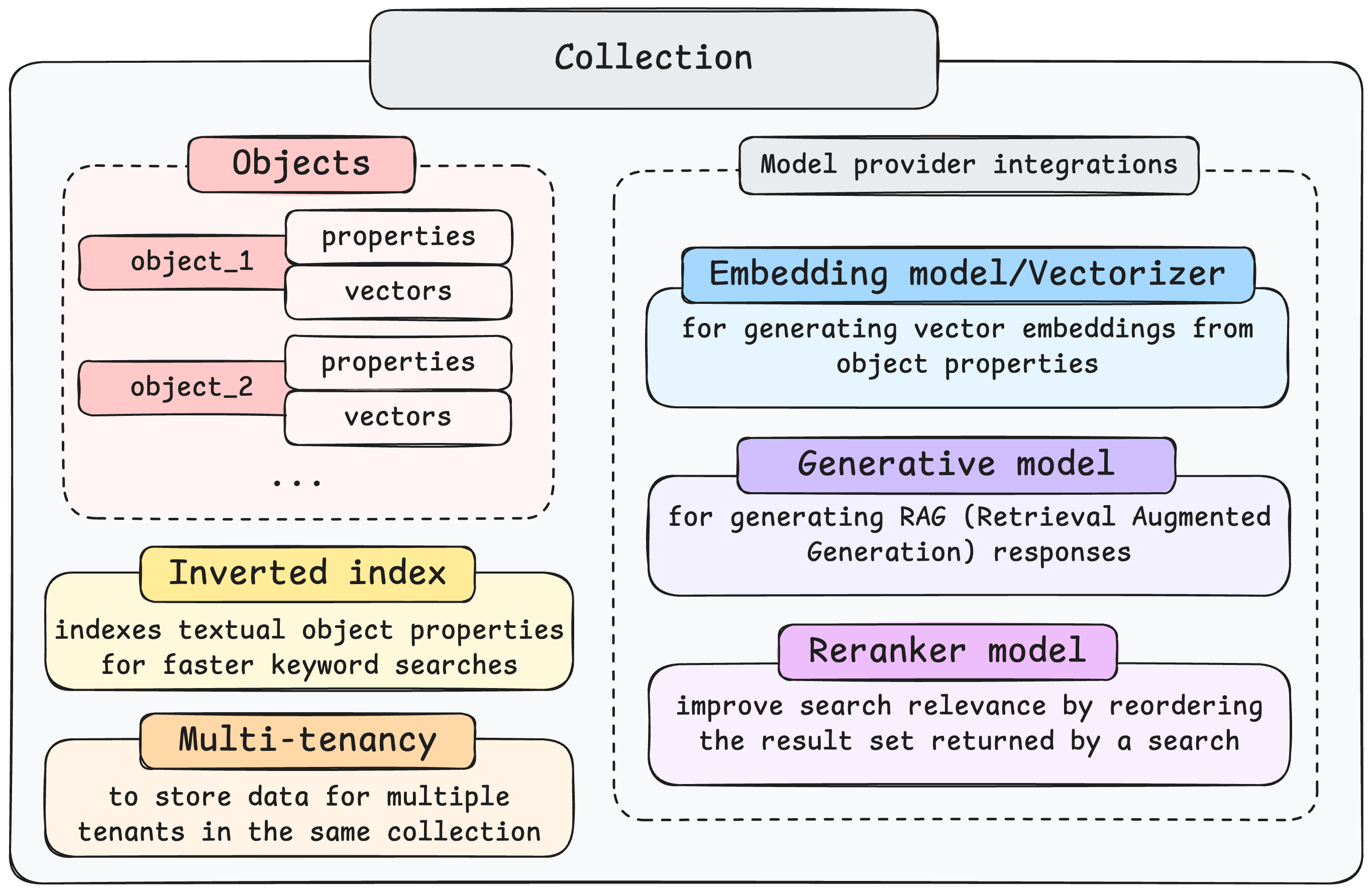
A Weaviate collection is defined by several core components and settings that enable data storage and vector search. Key elements include:
- Objects:
- The fundamental units stored within a collection. Each object contains data properties and includes vector embeddings representing its meaning. (See the 'How-to: Manage objects' guide for more details on manipulating objects).
- AI Model Integrations:
- Vectorizers (Embedding Models): Generate vector embeddings from object properties to enable semantic search.
- Generative models: Used to perform RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), combining retrieved data with generative AI capabilities.
- Reranker models: Refine search relevance by re-ordering the initial results from a search query.
- Configuration Settings:
- Vector index: The vector index is used to speed up vector searches.
- Inverted index: Optimizes keyword searches by indexing textual object properties for faster lookups.
- Multi-tenancy: Enables securely storing data for multiple distinct tenants (users or groups) within the same collection instance.
- Aliases: Use aliases to re-point to different collections without changing your application code.
Questions and feedback
If you have any questions or feedback, let us know in the user forum.
